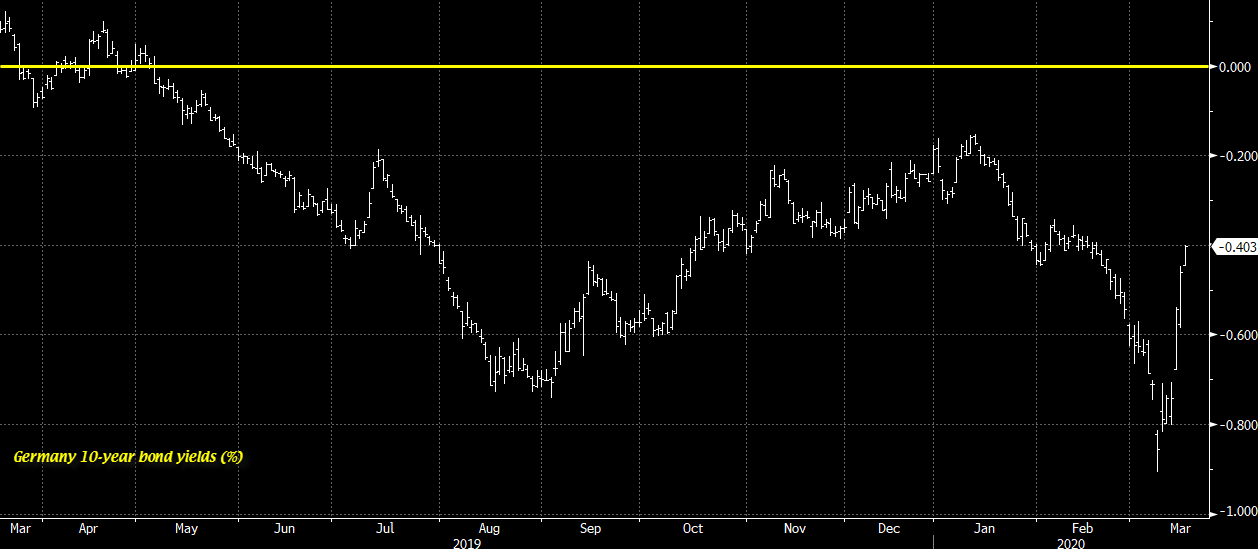
10-year German bond yields rise to its highest levels in a month

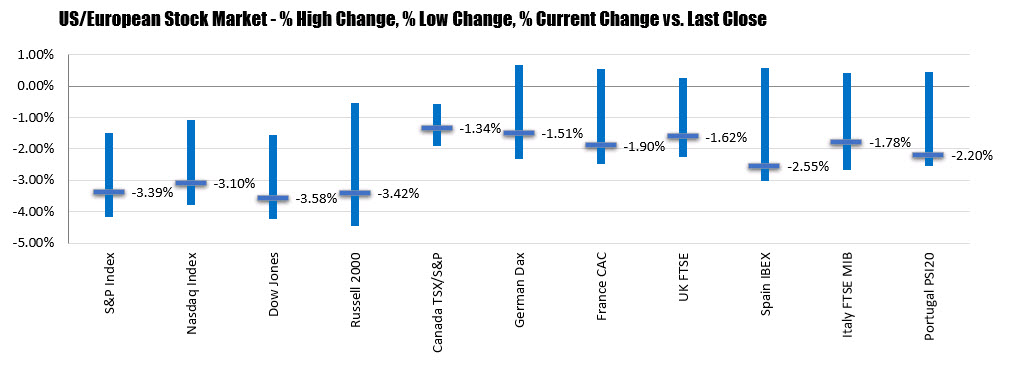
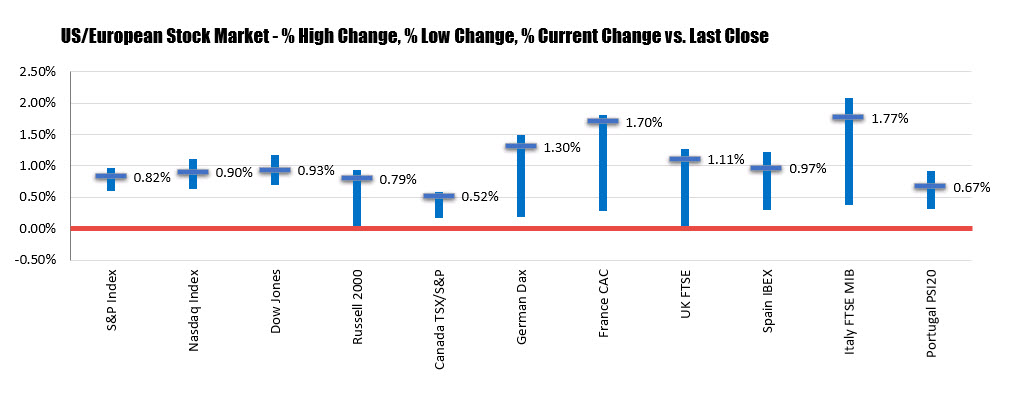
US stocks were mixed as Federal Reserve officials cast doubts on further rate cuts and a reading on domestic manufacturing stoked concerns over the health of the economy. The S&P 500 ticked 0.1 per cent lower after drifting between gains and losses, with investors turning their attention to the central bank’s annual summit where chairman Jay Powell will speak on Friday. The Nasdaq Composite was down 0.4 per cent, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average rose 0.2 per cent on a rally in shares of Boeing. Central bankers from around the world have descended on Jackson Hole, Wyoming, for a policy symposium that is closely watched by investors seeking clues on monetary policy.
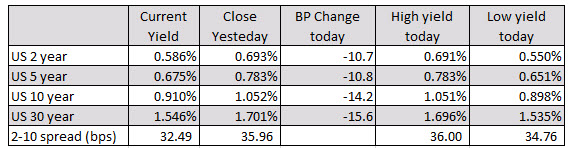
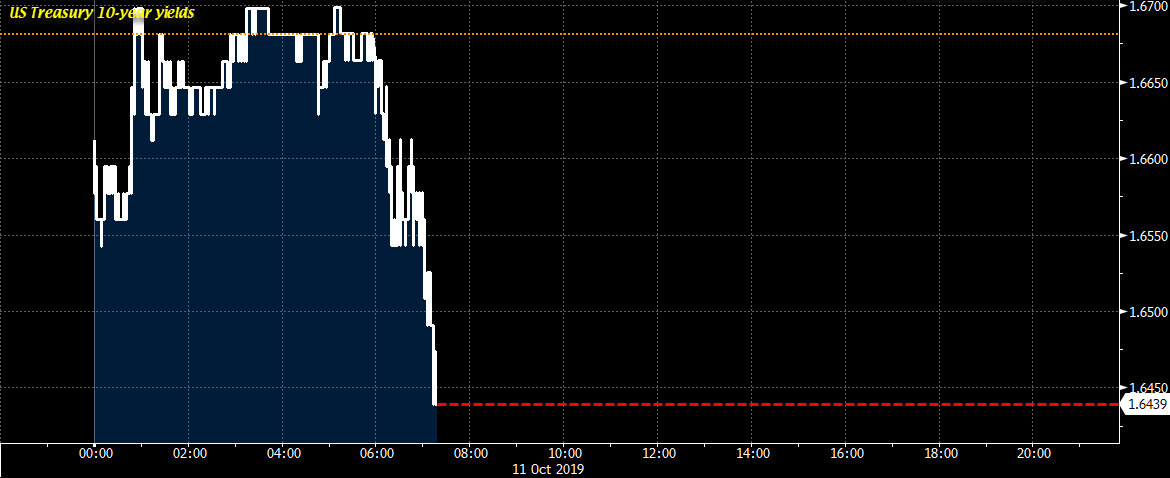
Market participants are looking for the Fed to follow its July rate cut with another one in September, but at the start of the Jackson Hole gathering on Thursday, Philadelphia Fed president Patrick Harker and Kansas City Fed president Esther George indicated in television interviews that they would not back further cuts. “My sense was we’ve added accommodation, and it wasn’t required in my view,” Ms George, one of two dissenters in the July decision, told CNBC. Mr Harker, who is not a voting member of the Fed’s policy setting committee, said he believes the federal funds rate is around its neutral level, adding: “I think we should stay here for a while and see how things play out.” The US 10- and two-year yield curve inverted for the second time this week following the remarks. The yield on the benchmark 10-year Treasury rose 3.3 basis points to 1.6097 per cent, while the policy-sensitive two-year yield was up 4.5bp at 1.6141 per cent. An inverted yield curve is considered a sign that investors expect a recession.
 Below are the changes and ranges for the US debt curve (from 2-30 years). The 2-10 spread is 1.53 bps currently, down from 4.32 bps at the close yesterday. The thing about today’s move is the yields are higher across the board with the shorter end up more due to the taking out more of the 50 BP cut idea.
Below are the changes and ranges for the US debt curve (from 2-30 years). The 2-10 spread is 1.53 bps currently, down from 4.32 bps at the close yesterday. The thing about today’s move is the yields are higher across the board with the shorter end up more due to the taking out more of the 50 BP cut idea.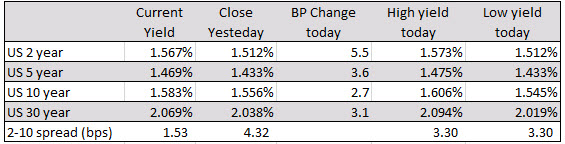
 1) Markets fall faster than they rise — and options traders know this. Otherwise, arbitraging this difference would be a meal for a lifetime.
1) Markets fall faster than they rise — and options traders know this. Otherwise, arbitraging this difference would be a meal for a lifetime.
2) Market participants perhaps anticipate that the realized volatility during a bear market is greater than a bull market. However, the problem with this analysis is one might expect to see an upward sloping volatility yield curve in out-of-the-money puts (during bull markets), and yet that does not usually occur based on my tests. Conversely, right now have a downward sloping yield curve in out of the money calls — which confirms the hypothesis that market participants anticipate slower price rises in the future. [Note to quants: I am not confusing delta, gamma and vega. I’m using options to predict terminal price at expiration.]
3) For most humans, fear of loss is a stronger emotion/motivator than the pleasure of gain (greed). This is well documented in the psychology and behavioral finance literature. Hence, ceterus paribus, capital market participants (who have a net long position) will, as a group, pull their rip cord faster — to flee from risk — than they will embrace the possibility of profit.
 Like other emerging market nations, it has entered a vicious cycle in which market skepticism creates higher borrowing costs and actually pushes the country closer to the abyss, its demise becoming a self fulfilling prophecy. Once that momentum begins, it is very hard to stop the decline in confidence.
Like other emerging market nations, it has entered a vicious cycle in which market skepticism creates higher borrowing costs and actually pushes the country closer to the abyss, its demise becoming a self fulfilling prophecy. Once that momentum begins, it is very hard to stop the decline in confidence. About the author: Cliff Wachtel