Paul Tudor Jones
Turned $1.5 million into $300 million in five years
 “That cotton trade was almost the deal breaker for me. It was at that point that I said, “Mr. Stupid, why risk everything on one trade? Why not make your life a pursuit of happiness rather than pain?”
“That cotton trade was almost the deal breaker for me. It was at that point that I said, “Mr. Stupid, why risk everything on one trade? Why not make your life a pursuit of happiness rather than pain?”
I had to learn discipline and money management. I decided that I was going to become very disciplined and businesslike about my trading. I spend my day trying to make myself as happy and relaxed as I can be.
If I have positions going against me, I get right out; if they are going for me, I keep them. I am always thinking about losing money as opposed to making money. Risk control is the most important thing in trading. I keep cutting my position size down as I have losing trades. (more…)
Archives of “January 31, 2019” day
rssNassim Taleb: Soros versus Buffett
If given a choice between investing with Buffett and billionaire investor George Soros, Taleb also said he would probably pick the latter.
“I am not saying Buffett isn’t as good as Soros,” he said. “I am saying that the probability Soros’s returns come from randomness is much smaller because he did almost everything: he bought currencies, he sold currencies, he did arbitrages. He made a lot more decisions. Buffett followed a strategy to buy companies that had a certain earnings profile, and it worked for him. There is a lot more luck involved in this strategy.”
[From: http://www.businessweek.com/news/2010-09-25/obama-s-stimulus-plan-made-crisis-worse-taleb-says.html]

I have high respect for your intelligence and thinking, and I believe that “Fooled by Randomness” and “The Black Swan” are must-read books for everyone. However, I believe your observation on Warren Buffett is wrong.
You justified your pick on Soros because you have observed his thousands if not millions of trades; therefore, giving you comfort that he is making decisions and his success, to quote what you said, is “2 million times more statistically evidence that his results are not by chance than Buffett does”.
You are implying that Soros is making thousands more decisions that Buffett. It seems to me that your understanding of Buffett is superficial, leading to your flawed conclusion.
During a meeting with MBA students from the University of Georgia in early 2007, Buffett told the group of students that “There were four Moody’s manuals at the time. I went through them all, page by page, over 10,000 pages twice. On page 1433, I found Western Insurance Securities. Its earnings per share were as follows: 1949 – $21.66, 1950 – $29.09. In 1951, the low-high share price was $3 – $13. Ten pages later, on page 1443, I found National American Fire Insurance….”
Again, in 2004, Buffett searched through the entire Korean stock market by reading Citigroup Investment Guide to Korean Stocks (that is over 1,700 companies). In 4 hours he found 20 companies that he liked and put $100 million to work.
These two examples illustrated that Buffett did make thousands of decisions of not to invest. Those who study Buffett intensely know that he works extreme hard and study all companies available from A to Z, leaving no stone unturned. Deciding not to buy is just as important as deciding to buy. However, inactivity is commonly misunderstood for not making any decision.
To quote Albert Einstein, “Not everything that counts can be counted, and not everything that can be counted, counts.”
How Bill Gates Made $350 Million At Age 30 During Microsoft's IPO
How hard is it to time the Market?
 As a simplified illustration of how hard it is to time the market, assume that you are 70% accurate calling market turns. If you are in the market, two calls are required: a sell and a subsequent buy. The probability of being correct (buying back in at a lower price than your selling price) is 70% times 70%, or 49%. That shows you have to be very good (and most people are not much better than a coin toss) to be successful at market timing.
As a simplified illustration of how hard it is to time the market, assume that you are 70% accurate calling market turns. If you are in the market, two calls are required: a sell and a subsequent buy. The probability of being correct (buying back in at a lower price than your selling price) is 70% times 70%, or 49%. That shows you have to be very good (and most people are not much better than a coin toss) to be successful at market timing.
Women in S&P 500 companies: CEOs 5.4% Top earners 9.5% Board seats 19.9% Executives 25.1%

Rules for Shorting
When it comes to shorting, many people are in the dark. It is more challenging to be short, subject to squeezes; the return max out at 100% — versus unlimited upside for longs.
Over the years, I have put together some rules for shorting. These are pretty broad and general, but they have kept me out of trouble when
Basic Rules for Shorting Stocks
1. Shorting Momentum names is dangerous: Unless you are Superman, never step in front of a speeding locomotive
2. Valuation alone is insufficient reason to get short a stock — History teaches us that cheap stocks can get cheaper, dear stocks can get more expensive
3. ALWAYS work with a pre-determined loss – either a physical or mental stop loss — Never leave yourself open to infinite losses
4. Fundamentals tell you WHY to short something, not WHEN to short it. ALWAYS have some technical confirmation before shorting. Make a short selling wish list, then WAIT for technical confirmation. (We use Money Flow, Short Term Trend lines, Institutional Ownership, Analyst Ratings).
5. It is tough to be a contrarian: During Bull and Bear cycles, the Crowd IS the market.
You have to figure out two things:
…a) When the crowd is wrong — Doug Kass calls it “Variant Perception”
…b) When the crowd starts to get an inkling they are wrong
At the turns — not the major trends — is where contrarians clean up.
6. Look for Over-owned, Over-loved stocks: 95% Institutional ownership, All buys or Strong Buys (no sells), and 700% gains over the past few years are reasons to put names on your short selling wish list. (That is how my partner Kevin Lane found and shorted Enron and Tyco back in the 1990s).
7. Beware the “Crowded Short“– they tend to become targets of the squeeze!
8. You can use Options to either juice your short returns, or pre-define your risk capital (options)
That is my short shorting list . . .
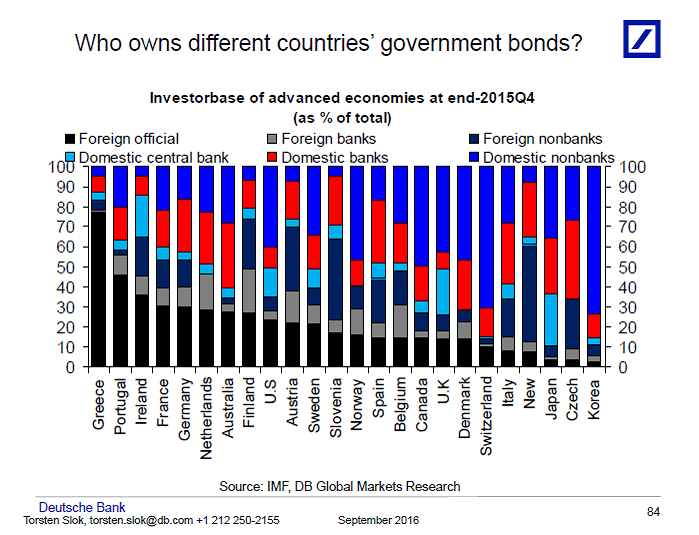
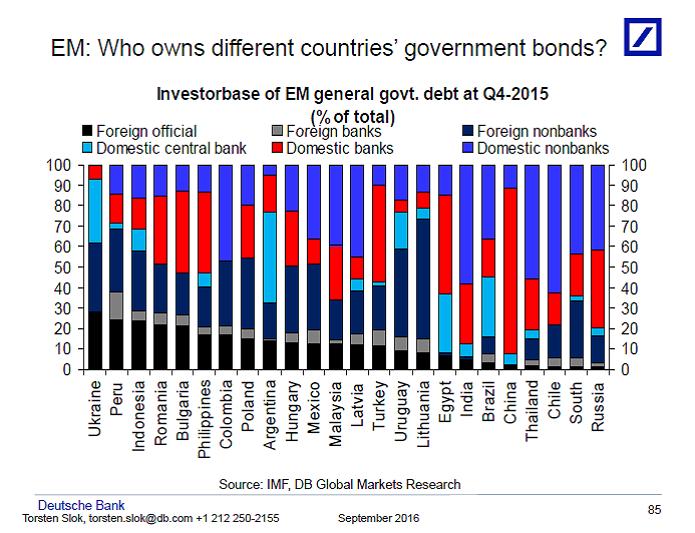
Who owns government bonds?
Cigarettes were promoted as being good for health, till early 1950s.

Logic of risk taking

Templeton’s 22 Principles For Successful Investing
- There is only one long term investment objective, maximum total after tax return.
- Success requires study and work. It’s harder than you think.
- Outperforming the majority of investors requires doing what they are not doing.
- Buy when pessimism is at its maximum, sell when optimism is at its maximum.
- Therefore, buy what most investors are selling.
- Buying when others have despaired, and selling when they are full of hope, takes fortitude.
- Bear markets aren’t forever. Prices usually turn up a year before the business cycle hits bottom.
- Popularity is temporary. When a sector goes out of fashion, it stays out for many years.
- In the long run, stock index prices fluctuate around the EPS trend line.
- Stock index earnings fluctuate around replacement book value for the stocks in the index.
- Buy what other people buy and you will succeed or fail as other people do.
- Timing: buy when short term owners have finished selling and sell when they’ve finished their buying, always opposing the fashion.
- Stock prices fluctuate more than values. So stock indexes will never produce the best total return performance.
- Focus on value because most investors focus on outlooks and trends.
- Invest worldwide.
- Stock price fluctuations are proportional to the square root of the price.
- Sell when you find a much better bargain to replace what you are selling.
- When your method becomes popular, switch to an unpopular method.
- Stay flexible. No asset or method is forever.
- Stock market investing takes more skill than any other kind of investing.
- A person can outperform a committee.
- If you begin with prayer, you will think more clearly and make fewer mistakes.