Latest Posts
rssWarrior Trading : Clifford Bennett
 These eight steps are intended as a guide to the new trader and a reminder to the experienced.
These eight steps are intended as a guide to the new trader and a reminder to the experienced.
1. Find Your Strength. It is important that the trader determine what type of market, trending or consolidating, best suits their own personality and strength. The best traders stay focused on one or the other and master it.
2. Know Your Market. You should know your market when trading. In other words, know the levels of support/resistance; know how the instrument you trade moves with the general market; know who is likely to be on the other side and what they are thinking; and “the terrain of any market includes the “long-term charts” (140).
3. Prepare Your Order. Know when to get into a trade and why and know when to get out of a trade and why. Just like a secret agent who will “never enter a room without knowing how to get out of it in a hurry” (142).
4. Placing Your Order. Once you have adequately prepared for a trade, it is then necessary to be ready to place the trade when the time is right. Here “patience is the key…you must be able to wait for the market to tell you when the moment is right. Wait for the market to generate the action; don’t force it” (143).
5. Sticking With Your Plan. This is probably the hardest part about trading. Once you enter the battlefield (enter a trade), the emotions of fear, ecstasy, greed, and sheer excitement can then take over and cause you to forget your well prepared plans for entry and exit. You must enter a “Zen-like mental state” where you remain in control of your emotions. Not doing so could spell disaster. (more…)
EMOTIONAL CYCLE OF MARKET PARTICIPANTS WITHOUT A PLAN /WITH A PLAN
Activity and Inactivity
I’ve noticed that my trading is more and more characterised by periods of doing a lot of trading, followed by periods of doing nothing except watching.
This seems to be a positive thing, as the old days consisted of trading every day no matter what the conditions, where as now I find that the markets will go into a mode that I just do not like the look of. In such cases if I try to force something, to “find a trade”, then I’ll get burned for sure.
To some degree I think this is because I have not yet spent much time on developing my strategies for trading insides large consolidation patterns. Of course it gets easier as they become more developed but by that time they are also getting old, and in the past I start making good trades in them just as they are about to end. The hard parts to trade are the start of trends / end of consolidation, and the end of trends / start of consolidation. These are times when the market is changing its basic mode, and are great places to lose money.
Diagnosing trading problems.
1) Problems of training and experience – Many traders put their money at risk well before they have developed their own trading styles based on the identification of an objective edge in the marketplace. They are not emotionally prepared to handle risk and reward, and they are not sufficiently steeped in markets to separate randomness from meaningful market patterns. They are like beginning golfers who decide to enter a competitive tournament. Their frustrations are the result of lack of preparation and experience. The answer to these problems is to develop a training program that helps you develop confidence and competence in identifying meaningful market patterns and acting upon those. Online trading rooms, where you can observe experienced traders apply their skills, are helpful for this purpose.
2) Problems of changing markets – When traders have had consistent success, but suddenly lose money with consistency, a reasonable hypothesis is that markets have changed and what once was an edge no longer is profitable. This happened to many momentum traders after the late 1990s bull market, and it also has been the case for many scalpers after volatility came out of the stock indices. Here the challenge is to remake one’s trading, either by retaining the core strategy and seeking other markets with opportunity or by finding new strategies for one’s market. The answer to these problems is to reduce your trading size and re-enter a learning curve to become acquainted with new markets and methods. Figuring out how you learned the markets initially will help you identify steps you need to take to relearn new patterns.
3) Situational emotional problems – These are emotional stresses that are recent in origin and that interfere with decision making and performance. Some of these stresses might pertain to trading, such as frustration after a slump or loss. Some might stem from one’s personal life, as in a relationship breakup or increased financial pressures due to a new home or child. Very often these problems create performance anxieties by putting the making of money ahead of the placing of good trades. The answer to these problems is to seek out short-term counseling to help you gain perspective on the problems and cope with them effectively. (more…)
Modi Wave :Business Sentiment Indicator..Going Down Down Down

JOHN KENNETH GALBRAITH ON STOCK MARKET MEMORY LOSS
 Where else but in the markets can short term memory loss be both beneficial and profitable?
Where else but in the markets can short term memory loss be both beneficial and profitable?
John Kenneth Galbraith, an economist, says the financial markets are characterized by…
“…extreme brevity of the financial memory. In consequence, financial disaster is quickly forgotten. In further consequence, when the same or closely similar circumstances occur again, SOMETIMES IN A FEW YEARS, they are hailed by a new, often youthful, and always extremely self-confident generation as a brilliantly innovative discovery in the financial and larger economic world. There can be few fields of human endeavor in which history counts for so little as in the world of finance.” [emphasis mine].
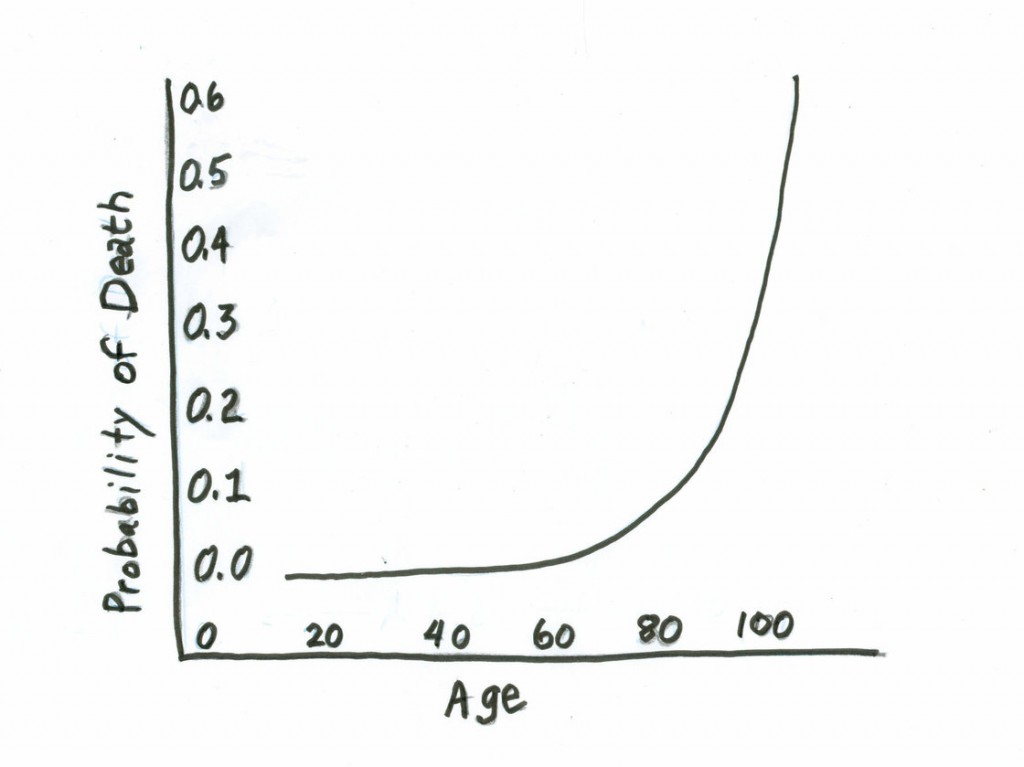
Every 8 Years, Your Chances of Dying Double
Robert Krulwich revisits the mysterious but true Gompertz Law of Human Mortality, named for the British actuary who had originally discovered this mathematical fact back in 1825.
via NPR:
Obviously, when you’re young (and past the extra-risky years of early childhood), the chances of dying in the coming year are minuscule — roughly 1 in 3,000 for 25-year-olds. (This is a group average, of course.)
But eight years later, the tables said, the odds will roughly double. ”When I’m 33 [the chances of my dying that year] will be about 1 in 1,500.”
And eight years after that…the odds double again: “It will be about 1 in 750.”
And eight years later, there’s another doubling. Looking down the chart, you’ll see that keeps happening and happening and happening. “Your probability of dying during a given year doubles every eight years.”
A helpful, if horrifying, chart:
Distribution goes logarithmic.

Coaching signals – math edition