Moody’s cuts the United Kingdom


The Federal Reserve is committed to using its full range of tools to support the U.S. economy in this challenging time, thereby promoting its maximum employment and price stability goals.
The COVID-19 pandemic is causing tremendous human and economic hardship across the United States and around the world. Economic activity and employment have picked up in recent months but remain well below their levels at the beginning of the year. Weaker demand and significantly lower oil prices are holding down consumer price inflation. Overall financial conditions have improved in recent months, in part reflecting policy measures to support the economy and the flow of credit to U.S. households and businesses.
The path of the economy will depend significantly on the course of the virus. The ongoing public health crisis will continue to weigh on economic activity, employment, and inflation in the near term, and poses considerable risks to the economic outlook over the medium term.
The Committee seeks to achieve maximum employment and inflation at the rate of 2 percent over the longer run. With inflation running persistently below this longer-run goal, the Committee will aim to achieve inflation moderately above 2 percent for some time so that inflation averages 2 percent over time and longer-term inflation expectations remain well anchored at 2 percent. The Committee expects to maintain an accommodative stance of monetary policy until these outcomes are achieved. The Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and expects it will be appropriate to maintain this target range until labor market conditions have reached levels consistent with the Committee’s assessments of maximum employment and inflation has risen to 2 percent and is on track to moderately exceed 2 percent for some time. In addition, over coming months the Federal Reserve will increase its holdings of Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities at least at the current pace to sustain smooth market functioning and help foster accommodative financial conditions, thereby supporting the flow of credit to households and businesses. (more…)
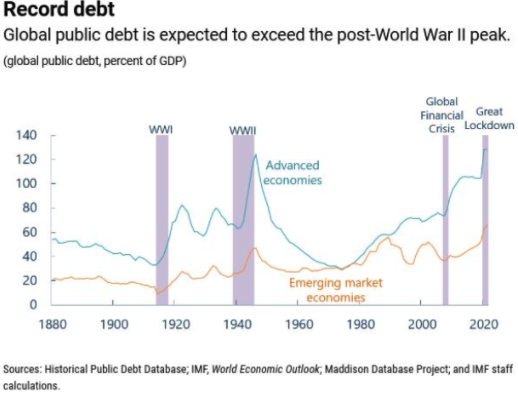
Debt levels are set to rise to unprecedented levels. According to the International Monetary Fund in June the public debt, as a share of GDP in advanced economies, is set to come in at over 130% for this year and next. To put that into perspective that surpasses the debt levels from the second world war.If you look at the chart below you can see that the double whammy of the Global Financial Crisis, followed by the present pandemic is pushing debt to record levels.
The population problem
The general thinking now is that the present crisis is a one in a hundred years kind of event (what if it isn’t) and that future generations will be able to claw back the debt levels over time. However, a publication from the Lancet in the UK suggests that there is a falling population that could fall by 9% at the end of the century. So, this means that there will be a large decline in numbers of working age adults. There are some countries which are projected to be particularly badly hit. Japan, Spain, Portugal, and Thailand are expected to see their populations halve by the end of the century. The countries which are projected to see 25% population declines are also projected to see a higher ration of older to younger people. So, more of this debt is going to be shouldered by fewer as an ageing population raises further spending considerations.
What will happen next?
There will be moves by governments to start to cap this debt problem. It will not be allowed to continue unless we get into worst disasters than we presently are in. The main concern is that of default. As long as willingness to repay remains, then the debt pile can be reduced. The main risk is if the debt becomes too great and the easiest solution is to just walk away…
GDP sa -7.8% q/q , a miss on already ugly low expectations
GDP annualised sa -27.8% q/q (ps when you see screaming headlines that Japan’s economy has shrunken 30% …. it hasn’t, but this is what the economically illiterate are referring to – you’ll know better)
GDP nominal -7.4% q/q
GDP deflator (an inflation indication) %
Private consumption -8.2%
Business spending -1.5% … if there is some not quite so bad news to take away from the data release this smaller than expected drop in capex is it
The Federal Reserve is committed to using its full range of tools to support the U.S. economy in this challenging time, thereby promoting its maximum employment and price stability goals.
The coronavirus outbreak is causing tremendous human and economic hardship across the United States and around the world. Following sharp declines, economic activity and employment have picked up somewhat in recent months but remain well below their levels at the beginning of the year. Weaker demand and significantly lower oil prices are holding down consumer price inflation. Overall financial conditions have improved in recent months, in part reflecting policy measures to support the economy and the flow of credit to U.S. households and businesses.
The path of the economy will depend significantly on the course of the virus. The ongoing public health crisis will weigh heavily on economic activity, employment, and inflation in the near term, and poses considerable risks to the economic outlook over the medium term. In light of these developments, the Committee decided to maintain the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent. The Committee expects to maintain this target range until it is confident that the economy has weathered recent events and is on track to achieve its maximum employment and price stability goals.
The Committee will continue to monitor the implications of incoming information for the economic outlook, including information related to public health, as well as global developments and muted inflation pressures, and will use its tools and act as appropriate to support the economy. In determining the timing and size of future adjustments to the stance of monetary policy, the Committee will assess realized and expected economic conditions relative to its maximum employment objective and its symmetric 2 percent inflation objective. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial and international developments.
To support the flow of credit to households and businesses, over coming months the Federal Reserve will increase its holdings of Treasury securities and agency residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities at least at the current pace to sustain smooth market functioning, thereby fostering effective transmission of monetary policy to broader financial conditions. In addition, the Open Market Desk will continue to offer large-scale overnight and term repurchase agreement operations. The Committee will closely monitor developments and is prepared to adjust its plans as appropriate.
Voting for the monetary policy action were Jerome H. Powell, Chair; John C. Williams, Vice Chair; Michelle W. Bowman; Lael Brainard; Richard H. Clarida; Patrick Harker; Robert S. Kaplan; Neel Kashkari; Loretta J. Mester; and Randal K. Quarles.
The IMF is out with a series of headlines on the US economy as the coronavirus risks increase. They say:
Dimon is correct on the unpreparedness. Three months of denial from the very top of the US administration that there was even a problem has cause such a tragic escalation in the numbers of lives lost.