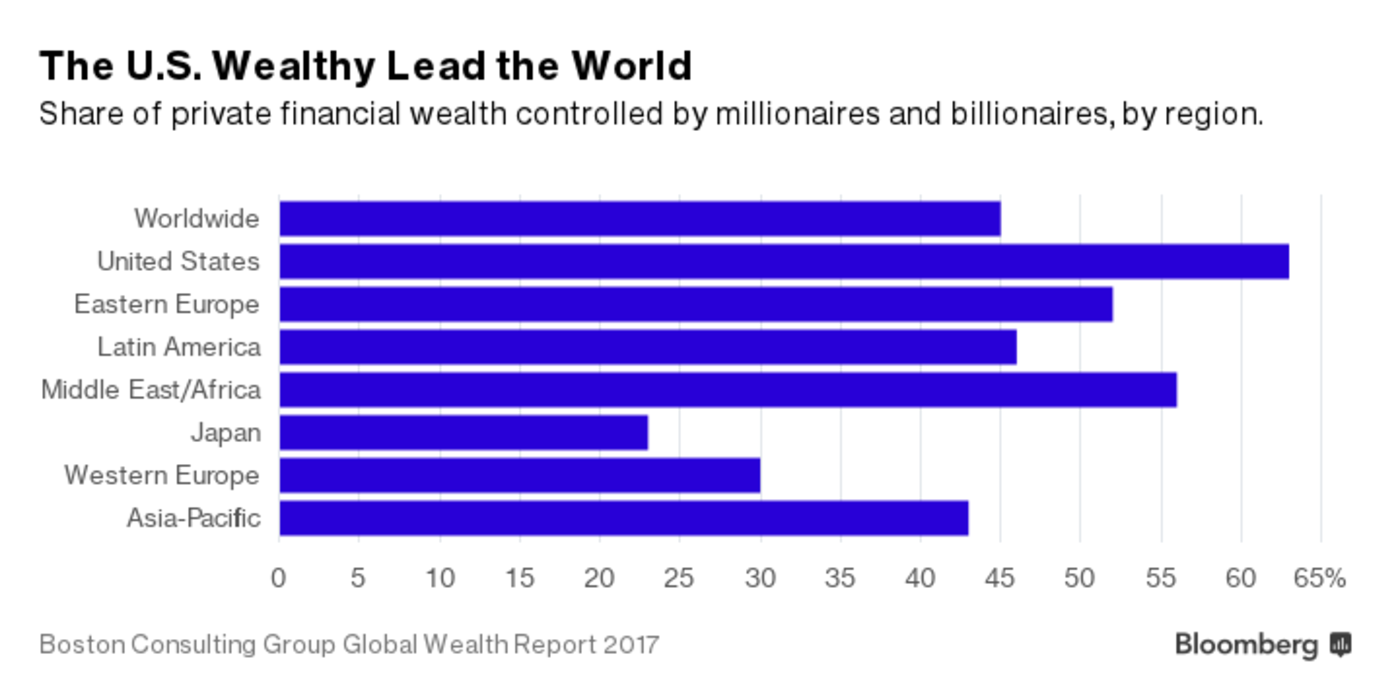
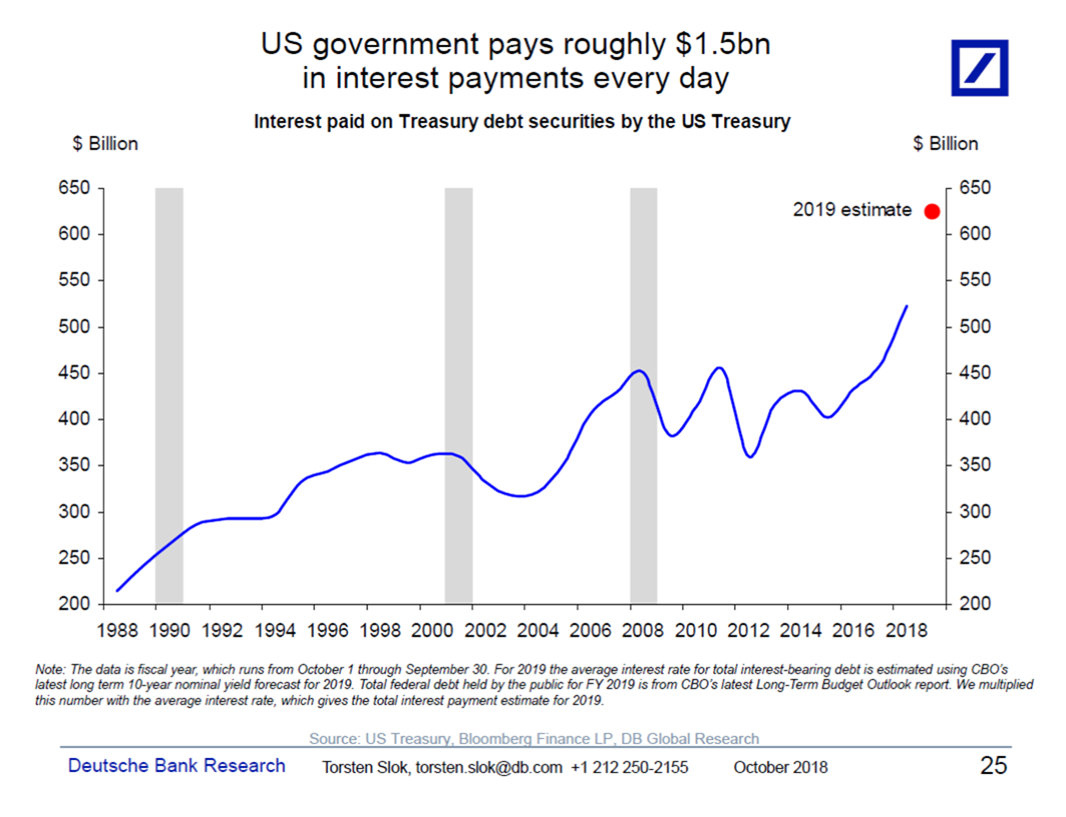
With all chart porn these days focusing on Europe, the Economist may have outdone itself with this combo set of all key financial and economic statistics for European countries.
Here is the caption provided by the Economist:
EUROPE is damned if it does and damned if it doesn’t, fiscally speaking. Fears that Greece’s debt crisis presage similar episodes elsewhere in the euro zone—notably in Portugal and Spain—have sent sovereign-bond yields for several southern European countries drifting higher, and have fuelled fears about the exposure of Europe’s banks to indebted governments. Attempts to rein in the public finances may calm bond markets but they also risk weakening growth, which makes life more difficult for exporters in places like China and America, and spells trouble of a different kind for the banks.
The interactive graphic above underlines some of the problems that the European economy faces. In 2009 only Poland of the 27 countries in the European Union managed to record positive growth. Although many countries have now returned to growth, it is generally anaemic. In many countries unemployment rates have not risen as much as you might expect given the depth of the crisis—there are times when making it hard to fire people has some advantages. But the flipside of labour-market rigidity is that the unemployment rate may be “sticky”, because firms have less need to hire as recovery takes hold. That will keep demand growth subdued.
Mediocre growth rates are more of a problem for some countries than others. They spell particular trouble for those that have high levels of debt and that do not have the option to devalue their currencies. That explains why Greece was first to lose the confidence of the markets: with a public-debt-to-GDP ratio of 115% and a budget deficit of 13.6% in 2009, it was the euro zone’s outlier country. Other countries are now scrambling to avoid Greece’s fate. Ireland, another heavily indebted euro-zone member, embarked on austerity early; Portugal and Spain, whose problems stem as much from levels of external and private debt as from government borrowing, have had their hands forced. Others still are pruning before the markets exert real pressure: Britain’s debt has the longest maturity of any EU member but it is still aiming to get its finances in order within four savage years.
Full chart after the jump





 I had the pleasure of reading a final finished copy of
I had the pleasure of reading a final finished copy of 

 NEW DELHI: India dropped two ranks to
NEW DELHI: India dropped two ranks to