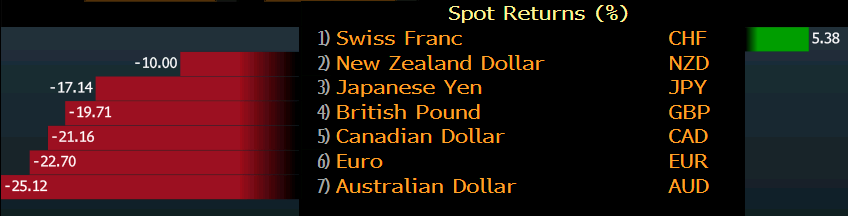
“Central banks have made a $6t commitment to prop up financial markets via asset purchases. That might not limit the collapse in EPS, but it might limit the collapse in share prices,” Citi says.

“Central banks have made a $6t commitment to prop up financial markets via asset purchases. That might not limit the collapse in EPS, but it might limit the collapse in share prices,” Citi says.

Market patterns don’t reverse in 10-year cycles like clockwork; there’s no guarantee that the coming decade will be the opposite of the one that just ended. But before you bet that the future will be like the past, it’s worth remembering that this decade hasn’t turned out the way investors predicted it would 10 years ago.
1. The most important single factor in shaping security markets is public psychology.
2. To make money in the stock market you either have to be ahead of the crowd or very sure they are going in the same direction for some time to come.
3. Accepting losses is the most important single investment device to insure safety of capital.
4. The difference between the investor who year in and year out procures for himself a final net profit, and the one who is usually in the red, is not entirely a question of superior selection of stocks or superior timing. Rather, it is also a case of knowing how to capitalize successes and curtail failures.
5. One useful fact to remember is that the most important indications are made in the early stages of a broad market move. Nine times out of ten the leaders of an advance are the stocks that make new highs ahead of the averages.
6. There is a saying, “A picture is worth a thousand words.” One might paraphrase this by saying a profit is worth more than endless alibis or explanations…prices and trends are really the best and simplest “indicators” you can find.
7. Profits can be made safely only when the opportunity is available and not just because they happen to be desired or needed.
8. Willingness and ability to hold funds uninvested while awaiting real opportunities is a key to success in the battle for investment survival.-
9. In addition to many other contributing factors of inflation or deflation, a very great factor is the psychological. The fact that people think prices are going to advance or decline very much contributes to their movement, and the very momentum of the trend itself tends to perpetuate itself.
10. Most people, especially investors, try to get a certain percentage return, and actually secure a minus yield when properly calculated over the years. Speculators risk less and have a better chance of getting something, in my opinion.
11. I feel all relevant factors, important and otherwise, are registered in the market’s behavior, and, in addition, the action of the market itself can be expected under most circumstances to stimulate buying or selling in a manner consistent enough to allow reasonably accurate forecasting of news in advance of its actual occurrence. The market is better at predicting the news than the news is at predicting the market
12. You don’t need analysts in a bull market, and you don’t want them in a bear market.
 Behavioral economics is now mainstream, at least outside of the stodgiest of economics departments. In fact, as the author writes, “This maturation of the field is so advanced that when this book is published in 2015, barring impeachment, I will be in the midst of a year serving as the president of the American Economic Association, and Robert Shiller will be my successor. The lunatics are running the asylum!” (p. 335) How behavioral economics got to this point from its humble, academically risky beginnings in the 1970s is the subject of Richard H. Thaler’s Misbehaving: The Making of Behavioral Economics (W. W. Norton, 2015).
Behavioral economics is now mainstream, at least outside of the stodgiest of economics departments. In fact, as the author writes, “This maturation of the field is so advanced that when this book is published in 2015, barring impeachment, I will be in the midst of a year serving as the president of the American Economic Association, and Robert Shiller will be my successor. The lunatics are running the asylum!” (p. 335) How behavioral economics got to this point from its humble, academically risky beginnings in the 1970s is the subject of Richard H. Thaler’s Misbehaving: The Making of Behavioral Economics (W. W. Norton, 2015).
Traditional economics studies rational agents, whom Thaler calls Econs; behavioral economics studies Humans. Econs are a construct designed to fit a theory; Humans are real people whose often irrational activities provide data (supposedly irrelevant factors) for study and hypothesis formation.
Thaler’s book, a personal history of the struggles and triumphs of behavioral economics, is also a wonderful introduction to the field. It recounts study after study that show just how predictably error-prone people are. And it explains how businesses can use these findings to keep customers happy and how governments can use them for the public good.
Looking back, Thaler suggests that the area where behavioral economics has had its greatest impact is in finance. “No one would have predicted that in 1980. In fact, it was unthinkable, because economists knew that financial markets were the most efficient of all markets, the places where arbitrage was easiest, and thus the domain in which misbehaving was least likely to appear.“ And yet these markets exhibited tell-tale anomalies, for instance the storied case of Palm and 3Com. Moreover, he notes, “It also didn’t hurt that financial markets offer the best opportunities to make money if markets are misbehaving, so a lot of intellectual resources have gone into investigating possible profitable investment strategies.” (p. 346)
The area where it has had the least impact so far is macroeconomics. In part, at least, this is due to the fact that the field “lacks the two key ingredients that contributed to the success of behavioral finance: the theories do not make easily falsifiable predictions, and the data are relatively scarce.” (p. 337)
Misbehaving is a thoroughly enjoyable read, not quite right for the beach but perfect for a rainy Sunday afternoon.
1. Make Rational, Not Emotional, Decisions — Do you have a plan to enter and exit your trades? Or do you just wing it? If you have a plan, write down your rules, and make sure that you trade your plan. If you don’t, or can’t, follow your rules, hire someone who can.
2. Respect Risk — Stock Market is not going anywhere. If you risk too much, your emotions will take over, and you will likely go broke. Always know where you are going to exit before you enter and how much you are going to risk if wrong.,
3. Don’t Judge Your Success One Trade at a Time — Losing money is part of trading. It happens to everyone. Once you learn to expect that will happen, you can plan for it and get past normal pitfalls, such as giving up on your system after a few losing trades.
4. Think like a winner — Remember that winning starts within. How you think is everything.,
5. Ask For Help — Making money on Wall Street is simple, but it is definitely not easy. Don’t let your ego get in your way of making money. Most people have a hard time asking for help. That’s just one reason why most people lose money on Stock Market . You don’t have to go it alone. Find someone you trust and are comfortable with, and don’t be afraid to ask for help.
1. Find and trade markets where your edge is the greatest.
2. Avoid markets were the probability of rule changes and lack of transparency is present.
3. Think of and imagine market scenarios others fail to.
4. Fundamental macroeconomic forces will ultimately prevail.
5. Trading time frames and profit objectives though must coincide with what the market is giving you at any one time.
6. Quantify risk with a multidimensional perspective, not just by one or two measures such as VAR or a price stop.
7. Learn from history. Jay Gould and his attempts to corner the gold markets in the late 1860’s. The Russian default of 1917 and 1998. The European Rate Mechanism break up. The Tequila crisis of 1994. The Asian financial crisis.
8. Be deadly serious, as Gichin Funakoshi said “You must be deadly serious in training”. If you have a position make it a meaningful size and monitor it carefully. I recall many comments from fellow traders the past few years saying something like “I am long EuroSwiss just to have some on but not really watching it.”
9. Define and use a trading methodology that incorporates a process and framework that works for you. Inclusive in this should be a daily routine that includes diet, exercise, family time, etc.
10. Seek out catalysts for CHANGE in markets. Where are the forces, in a Newtonian like law of motion, building up the greatest to cause a CHANGE and movement in markets?

The following speech was delivered by Ray Dalio of Bridgewater at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s 40th Annual Central Banking Seminar on Wednesday, October 5, 2016.
~~~
It is both an honor and a very special opportunity for me to be able to address such a large and esteemed group of central bankers at such an interesting time for central bankers. I especially want to thank President Dudley and Vice President Schetzel for inviting me to forthrightly share my perspective as an investor and my unconventional template that I believe sheds some light on the very unconventional circumstances that we face.
It is no longer controversial to say that:
• …this isn’t a normal business cycle and we are likely in an environment of abnormally slow growth
• …the current tools of monetary policy will be a lot less effective going forward
• …the risks are asymmetric to the downside
• …investment returns will be very low going forward, and (more…)