There are useful parallels between chess and trading. In the below quotation there is actually more than one lesson for those willing to consider it.
Pal Benko, a chess grandmaster said:
“Patience is the most valuable trait of the endgame player. In the endgame, the most common errors, besides those resulting from ignorance of theory, are caused by either impatience, complacency, exhaustion, or all of the above.”
1) Ignorance of theory
2) Impatience / Patience
3) Complacency
4) Exhaustion
See this 1 chess lesson morphed into 4 lessons:
Let me have a little go at highlighting some things that we can perhaps learn from this chess quote that apply to trading. (I’d love it if you told me yours in the comment section below. Go on, be brave and join in – dialogue is good :-))
1) Ignorance of Theory
Ed Seykota has been recorded as saying something like: until you master the basic literature and spend some time with successful traders, you might consider confining your trading to the supermarket.
Naturally with trading, getting comfortable with the basics is an important step. Make sure, however, not to end up one of those paralysed and stuck in student mode. At some point you have to be willing to move from student to trader. One of the useful ways of ‘spending time with traders’ if you are not employed in a trading firm is to utilise things like Stocktwits, trading groups, forums etc. (more…)


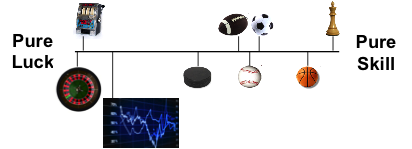
 Why do the gurus who proclaim a “feel” for the market tell us to eliminate emotions from trading?
Why do the gurus who proclaim a “feel” for the market tell us to eliminate emotions from trading?
 As an avid fan of the game of the KINGS, I have never paid attention before between the amazing similarities between chess and trading, until I read a BRUCE PANDOLFINI book called “Every move must have it’s purpose”
As an avid fan of the game of the KINGS, I have never paid attention before between the amazing similarities between chess and trading, until I read a BRUCE PANDOLFINI book called “Every move must have it’s purpose”